DLTS Method
DLTS (Deep Level Transient Spectroscopy) Method:
Since the characteristics of semiconductor materials are greatly affected by very small impurities such as inherent lattice defects (crystal defects), defect evaluation is extremely important.
Since it was devised by Lang of Bell Laboratories in 1974, the DLTS method is an excellent technique to detect the electronic state (deep level) created by crystal defects with high sensitivity, and continues to be widely used.
In the DLTS method, according to its measurement principle, samples having a so-called semiconductor junction (a Schottky or pn junction etc.) are used.
By monitoring the dynamic process by which the carrier (e.g. electron) trapped in the deep level is emitted into the band (conduction band), through the transient changes in the junction capacitance of the sample, the parameters (energy levels, capture cross-section) and concentration value, spatial distribution etc. of the level can be known.
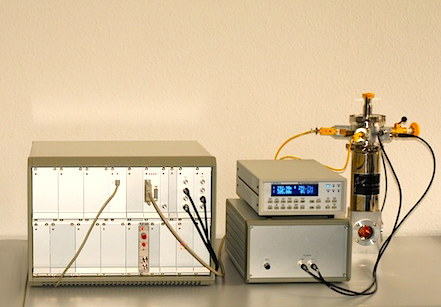
As well, the DLTS method is not only effective for measurement of discrete levels produced by single atom level defects, but also for evaluating interface states in MOS structures and continuum levels in amorphous semiconductors.
Furthermore, a feature of the DLTS method is that it's superior sensitivity levels can be heightened.
The impure atom detection lower limit concentration level detected by SIMS analysis, (high sensitivity surface analysis) is 10E14 atoms / cm3, however, amazingly, in the DLTS method, levels of trace concentrations of 10E9 atoms / cm3 or less can be detected depending on the conditions.
(DLTS法に関するより詳細な解説は、別項をご覧ください)
